Software Bug Wikipedia
Contents. History Usage of the 'alpha/beta' test terminology originated.
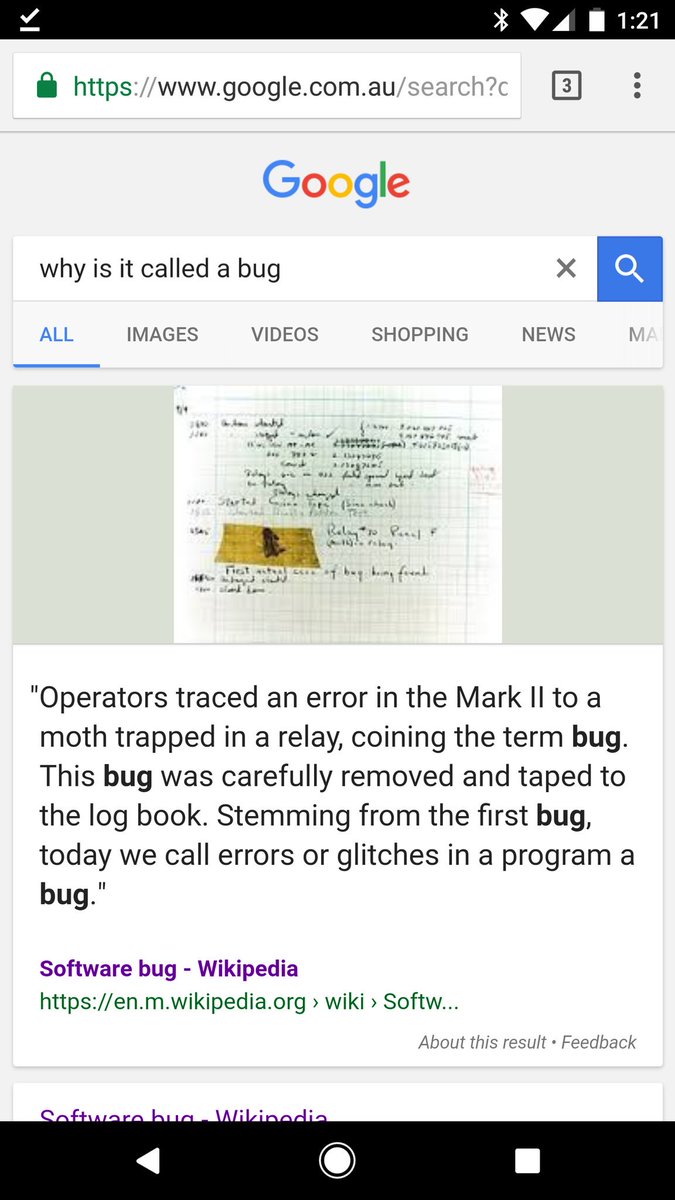
A software bug is a problem with the code in a computer program which makes it not work properly. They can cause inconvenience to the user and may make their computer.
As long ago as the 1950s (and probably earlier), IBM used similar terminology for their hardware development. 'A' test was the verification of a new product before public announcement.
'B' test was the verification before releasing the product to be manufactured. 'C' test was the final test before general availability of the product. As software became a significant part of IBM's offerings, the alpha test terminology was used to denote the pre-announcement test and beta test was used to show product readiness for general availability.
Martin Belsky, a manager on some of IBM's earlier software projects claimed to have invented the terminology. IBM dropped the alpha/beta terminology during the 1960s, but by then it had received fairly wide notice.
The usage of 'beta test' to refer to testing done by customers was not done in IBM. Rather, IBM used the term 'field test'. Stages of development Pre-alpha Pre-alpha refers to all activities performed during the software project before formal testing. These activities can include, and. In typical development, there are several types of pre-alpha versions. Milestone versions include specific sets of functions and are released as soon as the functionality is complete.
Alpha The alpha phase of the release life cycle is the first phase to begin (alpha is the first letter of the, used as the number 1). In this phase, developers generally test the software using. Additional validation is then performed using or techniques, by another testing team. Moving to black-box testing inside the organization is known as alpha release. Alpha software can be unstable and could cause crashes or data loss. Alpha software may not contain all of the features that are planned for the final version. In general, external availability of alpha software is uncommon in, while often has publicly available alpha versions.
The alpha phase usually ends with a, indicating that no more features will be added to the software. At this time, the software is said to be.
'Beta Test' redirects here. For the film, see. Beta, named after the second letter of the Greek alphabet, is the software development phase following alpha. Software in the beta stage is also known as betaware. Beta phase generally begins when the software is but likely to contain a number of known or unknown bugs.
Software in the beta phase will generally have many more bugs in it than completed software, as well as speed/performance issues and may still cause crashes or data loss. The focus of beta testing is reducing impacts to users, often incorporating. The process of delivering a beta version to the users is called beta release and this is typically the first time that the software is available outside of the organization that developed it. Beta version software is often useful for demonstrations and previews within an organization and to prospective customers. Some developers refer to this stage as a preview, preview release, prototype, technical preview / technology preview ( TP), or early access. Some software is kept in, where new features and functionality are continually added to the software without establishing a final 'stable' release. Beta testers are people who actively report issues of beta software.
They are usually customers or representatives of prospective customers of the organization that develops the software. Beta testers tend to volunteer their services free of charge but often receive versions of the product they test, discounts on the release version, or other incentives. As the has facilitated rapid and inexpensive distribution of software, companies have begun to take a looser approach to use of the word 'beta'. In February 2005, published an article about the recent phenomenon of a beta version often staying for years and being used as if it were in production level, disparagingly called 'perpetual beta'. It noted that and, for example, had been in beta for a long period of time and were not expected to drop the beta status despite the fact that they were widely used; however, Google News did leave beta in January 2006, followed by, including Gmail, in July 2009. This technique may allow a developer to delay offering full support and responsibility for remaining issues. In the context of, people even talk of perpetual betas to signify that some software is meant to stay in beta state.
Also, 'beta' is sometimes used to indicate something more like a, or as a form of time-limited demo, or marketing technique. Since the introduction of, has no longer been naming their software as a beta. Instead, they have been using the term preview for most pre-release software. Since the launch of the back in 2014, all pre-release builds that are released through the program are known as Insider Preview builds. Open and closed beta Developers release either a closed beta also called private beta or an open beta also called public beta; closed beta versions are released to a restricted group of individuals for a user test by invitation, while open beta testers are from a larger group, or anyone interested. Private beta could be suitable for the software that is capable to deliver value, but is not ready to be used by everyone either due to scaling issues, lack of documentation or still missing vital features.
The testers report any bugs that they find, and sometimes suggest additional features they think should be available in the final version. Examples of a major public beta test include the following:. Early customers purchased a 'pioneer edition' of the WordVision word processor for the for $49.95. In 1984, wrote that 'in a brilliant marketing coup, Bruce and James Program Publishers managed to get people to pay for the privilege of testing the product.' . In September 2000 a boxed version of 's operating system was released.
's release of community technology previews ( CTPs) for, between September 2005 and May 2006. Throughout 2009 to 2011, was in public beta. On December 29, 2014, all owners of for the were able to download and play the Beta of for free through January 18, 2015. Users of the Beta were reminded via an in-game popup that the release was a Beta and could contain some glitches, and were encouraged to communicate them through the online community. Open betas serve the dual purpose of demonstrating a product to potential consumers, and testing among an extremely wide user base likely to bring to light obscure errors that a much smaller testing team might not find. Release candidate A release candidate ( RC), also known as 'going silver', is a beta version with potential to be a final product, which is ready to release unless significant emerge.
In this stage of product stabilization, all product features have been designed, coded and tested through one or more beta cycles with no known showstopper-class bugs. A release is called code complete when the development team agrees that no entirely new source code will be added to this release. There could still be source code changes to fix defects, changes to documentation and data files, and peripheral code for test cases or utilities. Beta testers, if privately selected, will often be credited for using the release candidate as though it were a finished product. Beta testing is conducted in a client's or customer's location and to test the software from a user's perspective. Release Once released, the software is generally known as a 'stable release'.
The formal term often depends on the method of release: physical media, online release or a web application. Release to manufacturing (RTM) The term 'release to manufacturing', also known as 'going gold', is a term used when a software product is ready to be delivered. This build may be, allowing the end user to verify the integrity and authenticity of the software purchase. A copy of the RTM build known as the 'gold master' or GM is sent for mass duplication if applicable.
RTM precedes general availability (GA) when the product is released to the public. It is typically used in certain retail mass-production software contexts—as opposed to a specialized software production or project in a commercial or government production and distribution—where the software is sold as part of a bundle in a related computer hardware sale and typically where the software and related hardware is ultimately to be available and sold on mass/public basis at retail stores to indicate that the software has met a defined quality level and is ready for mass retail distribution. RTM could also mean in other contexts that the software has been delivered or released to a client or customer for installation or distribution to the related hardware end user computers or machines. The term does not define the delivery mechanism or volume; it only states that the quality is sufficient for mass distribution. The deliverable from the engineering organization is frequently in the form of a golden master media used for duplication or to produce the image for the web. General availability (GA).
Milestones in a product life cycle: general availability (GA), (EOLA), (LOD), and (EOL) General availability ( GA) is the marketing stage at which all necessary activities have been completed and a software product is available for purchase, depending, however, on language, region, electronic vs. Media availability. Commercialization activities could include security and compliance tests, as well as localization and worldwide availability. The time between RTM and GA can be from a week to months in some cases before a generally available release can be declared because of the time needed to complete all commercialization activities required by GA. At this stage, the software has 'gone live'. Release to web (RTW) Release to the web (RTW) or web release is a means of software delivery that utilizes the Internet for distribution.
No physical media are produced in this type of release mechanism by the manufacturer. Web releases are becoming more common as Internet usage grows. Support During its supported lifetime, software is sometimes subjected to service releases, or, sometimes also called 'interim releases'.
For example, Microsoft released three major service packs for the editions of and two service packs for the editions. Such service releases contain a collection of updates, fixes, and enhancements, delivered in the form of a single installable package.
They may also implement new features. Some software is released with the expectation of regular support.
Classes of software that generally involve protracted support as the norm include and. A good example of a game that utilizes this process is, an developed by, which features regular 'updates' featuring new content and bug fixes. End-of-life. From the original on 2011-04-27. Retrieved 2011-01-12. 'The Next Generation 1996 Lexicon A to Z'.
Alpha software generally barely runs and is missing major features like gameplay and complete levels. Retrieved 2015-04-06. 'The Next Generation 1996 Lexicon A to Z'.
Retrieved 2015-03-18. Archived from on 2006-05-15. Google Blog.
From the original on 21 January 2011. Retrieved 2011-01-12. 2011-04-30 at the. (1984-04-03). From the original on 17 March 2015.
Retrieved 15 February 2015. (Press release). 13 September 2000. From the original on 1 May 2011. Retrieved 2011-02-22. (Press release).
October 2005. From the original on 2011-04-30.
Retrieved 2011-02-22. Luxembourg, Yvan Philippe (20 May 2013). From the original on 10 August 2013.
Retrieved 21 May 2013. Bibliography. Continuous Delivery: Reliable Software Releases through Build, Test, and Deployment Automation by Jez Humble, David Farley.

Contents. Space exploration. A booster went off course during launch, resulting in the destruction of. This was the result of the failure of a transcriber to notice an overbar in a written specification for the guidance program, resulting in the coding of an incorrect formula in its software. (July 22, 1962).
Note that the initial reporting of the cause of this bug was incorrect. The 's deactivated its attitude thrusters and could no longer properly orient its solar arrays or communicate with Earth, eventually depleting its batteries. (September 10, 1988).
The 's was destroyed 40 seconds after takeoff (June 4, 1996). The US$1 billion prototype rocket self-destructed due to a bug in the on-board guidance software.
Iphone X Software Bug
NASA was destroyed because its flight software mistook vibrations due to atmospheric turbulance for evidence that the vehicle had landed and shut off the engines 40 meters from the Martian surface (December 3, 1999). Its sister spacecraft was also destroyed, but due to human error and not, as is sometimes reported, due to a software bug. A mis-sent command from Earth caused the software of the NASA to incorrectly assume that a motor had failed, causing it to point one of its batteries at the sun - subsequently overheating it. (November 2, 2006). Medical. A bug in the code controlling the machine was directly responsible for at least five patient deaths in the 1980s when it administered excessive quantities of X-rays.
A heart device was found vulnerable to remote attacks in March 2008. Computing. The spawned fears of worldwide economic collapse and an industry of consultants providing last-minute fixes. In addition, it is possible the problem could recur in (the ), as many systems calculate the time in seconds since 1 January 1970, and store this figure as a, for which the maximum possible value is 2 31 (2,147,483,648). Electric power transmission. The was triggered by a local outage that went undetected due to a in General Electric Energy's XA/21 monitoring software. Telecommunications.
long distance network crash (January 15, 1990), in which the failure of one switching system would cause a message to be sent to nearby switching units to tell them that there was a problem. Unfortunately, the arrival of that message would cause those other systems to fail too - resulting in a 'wave' of failure that rapidly spread across the entire AT&T long distance network. In January 2009, 's search engine erroneously notified users that every web site world wide was potentially malicious, including its own. Military.
The, caused its system clock to drift by one third of a second - resulting in failure to locate and intercept an incoming missile. The scud impacted in a military compound in, (February 25, 1991), killing 28 Americans. A in June 1994. A Royal Air Force helicopter crashed into the Mull of Kintyre, killing 29. This was initially dismissed as pilot error, but an investigation by uncovered sufficient evidence to convince a inquiry that it may have been caused by a software bug in the aircraft's. was left dead in the water in 1998 for nearly 3 hours after a error.
In April 1992 the first crashed while landing at, California. The cause of the crash was found to be a flight control that failed to prevent a. While attempting its first overseas deployment to the in Okinawa, Japan, on 11 February 2007, a group of six flying from, Hawaii, experienced multiple computer crashes coincident with their crossing of the 180th meridian of (the ).
The computer failures included at least navigation (completely lost) and communication. The fighters were able to return to Hawaii by following their, something that might have been problematic had the weather not been good. The error was fixed within 48 hours, allowing a delayed deployment. Media. 's deployment of the Trinity patch, which erased the boot.ini file from several thousand users' computers, rendering them unable to boot.

This was due to the usage of a within the game that was also named boot.ini. As such, the deletion had targeted the wrong directory instead of the /eve directory. In the , produced a music that employed a scheme that covertly installed a ' on any Windows PC that was used to play it. Their intent was to hide the copy protection mechanism to make it harder to circumvent.
Unfortunately, the rootkit inadvertently opened a security hole resulting in a wave of successful attacks on the computers of those who had innocently played the CD. Sony's subsequent efforts to provide a utility to fix the problem actually exacerbated it.
Software Bug Management
Encryption. In order to fix a warning issued by, a maintainer of patched and broke the random number generator in the process.
The patch was uploaded in September 2006 and made its way into the official release; it was not reported until April 2008. Every key generated with the broken version is compromised, as is all data encrypted with it, threatening many applications that rely on encryption such as, or protected connections and. Retrieved 2008-01-07. Hints on Programming Language Design. In Sigact/Sigplan Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages. October 1973., reprinted in Horowitz.
Western Union Software Bug
Programming Languages, A Grand Tour, 3rd ed. Retrieved 2008-01-07. Zakharov (1989). 'Brief history of the Phobos mission'. Nature 341: 581–585.:. (March 1997 ). 'The Ariane 5 Software Failure'.
Software Engineering Notes 22 (2): 84.:. Retrieved 2008-01-07. Retrieved 2008-10-19.
Retrieved 2008-01-07. Retrieved January 11, 2007. Retrieved 2008-01-07. Retrieved 2008-01-07.
Retrieved 2008-01-07. Retrieved 2008-09-28. Retrieved 2008-01-07. Retrieved 2008-01-12. Retrieved 2008-01-07.
Sterling, Bruce.: Law and Disorder on the Electronic Frontier (ISBN 0-553-56370-X). Spectra Books. Retrieved 2008-05-15.
Robert Skeel. SIAM News, volume 25, nr 4. Retrieved 2008-09-30. Retrieved 2008-01-07. Retrieved 2008-01-07.
f-22raptor.com. Retrieved: 23 July 2009. Air Force, 26 February 2007. Retrieved 2008-03-08.
JDBC Driver – Type 2 ( Part Native Driver ) This is an approach wherein the implemented class in Java makes calls to the code written from the database provider. Jdbc connectivity by type 4 driver Jdbc connectivity by type 4 driver I have done a code with database connectivity with driver 4,it copiles,but while running it is. Driver class in java. Using the Oracle Type 4 JDBC drivers with the Java Security Manager enabled requires. The application and driver code bases must be granted security. JDBC driver in type 4 mode is. All Java/Net-protocol driver. Type 3 database requests are passed through the network to the. This was liked by Database vendors though because they can reuse there existing native libraries. Java/Net- protocol driver or Type 3 JDBC driverboth type 1 and type 2 JDBC drivers were not written in Java so there.
Retrieved 2008-05-15., Mark's Blog, November 4, 2005, retrieved November 22, 2006. Retrieved 2008-04-16.